Table of Contents
Introduction
A water pump is a crucial component in both automotive and industrial applications, responsible for circulating coolant or water to maintain optimal temperatures. Whether it’s in a vehicle’s cooling system or an industrial setup, a water pump plays a vital role in ensuring smooth operation.
- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Key Components of a Water Pump 🔍
- 1. Housing (Pump Body) 🏠
- 2. Impeller 🚀
- 3. Bearing Assembly ⚙️
- 4. Shaft 🚗
- 5. Seal and Gaskets 🔧
- 6. Pulley or Drive Mechanism 🏎️
- 7. Inlet and Outlet Ports 🔄
- How a Water Pump Works 🔄
- Importance of a Well-Functioning Water Pump 🚗
- Common Issues and Signs of Water Pump Failure ⚠️
- Conclusion
In this guide, we’ll break down the components of a water pump, explain how it functions, and discuss the importance of proper maintenance. Understanding what’s inside a water pump can help you diagnose issues, make informed purchasing decisions, and improve performance.
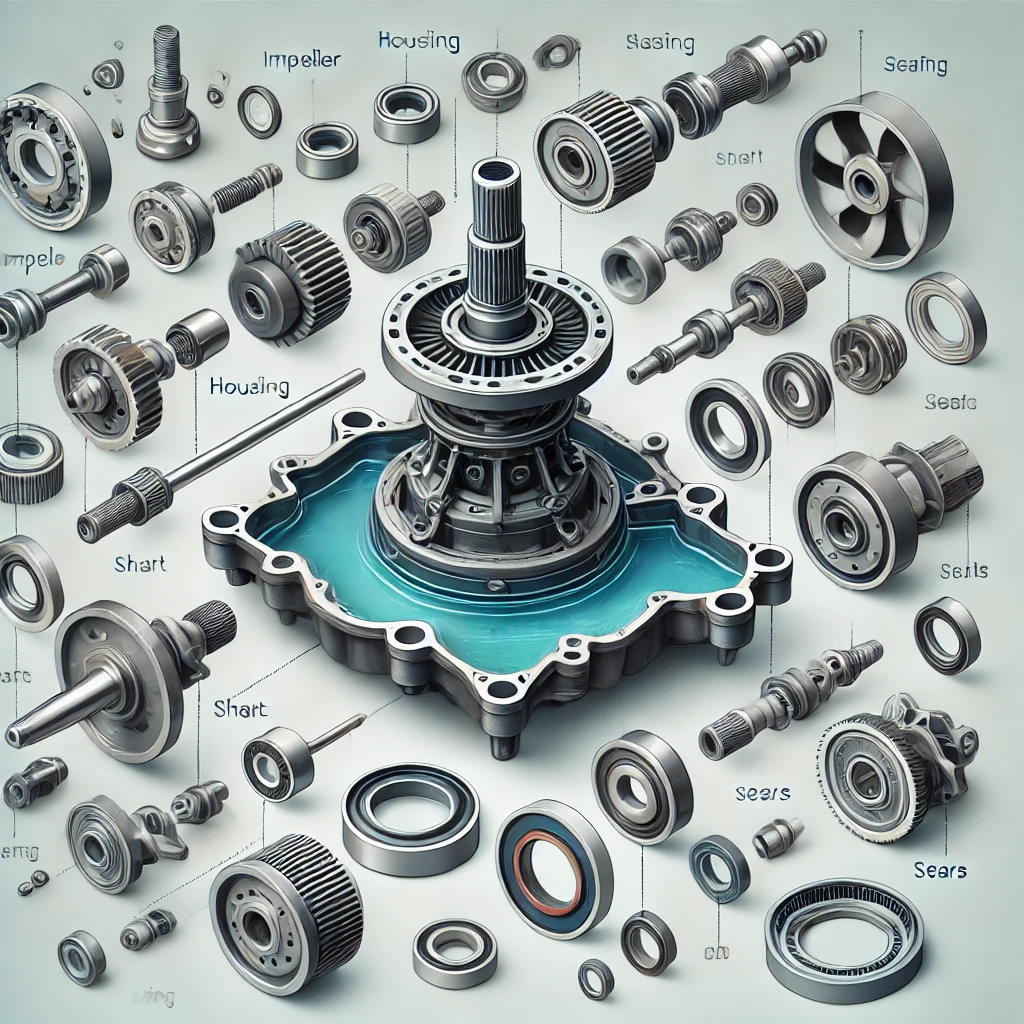
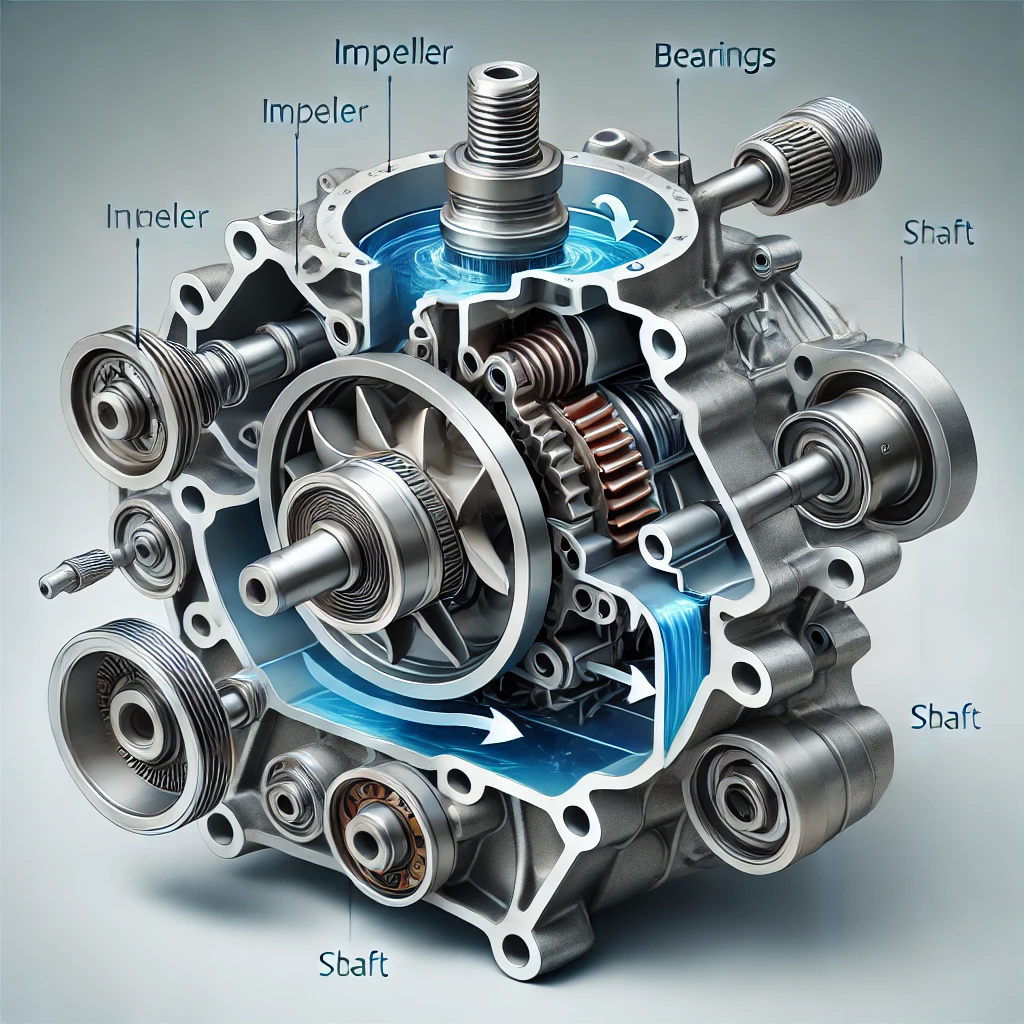
Key Components of a Water Pump 🔍
A typical water pump consists of several essential parts, each contributing to its operation:
1. Housing (Pump Body) 🏠
The housing is the outer shell that encases all internal components. It’s typically made from cast aluminum, cast iron, or reinforced plastic, providing durability and heat resistance.
2. Impeller 🚀
The impeller is the heart of the water pump. It’s a rotating component, usually made of metal or composite materials, that pushes coolant through the system. The impeller has blades or vanes that create centrifugal force, propelling the liquid outward.
3. Bearing Assembly ⚙️
The bearing ensures smooth rotation of the impeller. It reduces friction and allows the shaft to spin freely. A worn-out bearing can lead to unusual noises and eventual pump failure.
4. Shaft 🚗
The shaft connects the impeller to the drive mechanism, which is usually powered by a serpentine belt, timing belt, or electric motor. It transmits rotational force from the engine or motor to the impeller.
5. Seal and Gaskets 🔧
Seals and gaskets prevent coolant leakage and ensure a tight fit between the pump components. These are usually made of rubber, silicone, or metal-reinforced materials to withstand temperature variations and pressure changes.
6. Pulley or Drive Mechanism 🏎️
The pulley or drive mechanism is what powers the pump. In automotive applications, it’s typically driven by a serpentine belt or timing belt. In industrial settings, it may be powered by an electric motor.
7. Inlet and Outlet Ports 🔄
Water pumps have inlet and outlet ports that control the direction of coolant flow. The inlet draws coolant from the radiator or cooling reservoir, while the outlet sends it through the system.
How a Water Pump Works 🔄
The water pump operates using centrifugal force to circulate coolant or water. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
- The engine or motor drives the pump via a belt or electric motor.
- The impeller spins, creating centrifugal force that pushes coolant outward.
- Coolant is drawn from the radiator or reservoir through the inlet port.
- The pressurized coolant is forced through the outlet port and circulated through the system.
- The coolant absorbs heat from the engine or machinery and returns to the radiator for cooling.
This continuous cycle ensures that the engine or industrial equipment maintains an optimal operating temperature.
Importance of a Well-Functioning Water Pump 🚗
A faulty water pump can lead to engine overheating, system inefficiencies, and severe damage. Here’s why a properly functioning water pump is essential:
- Prevents Overheating 🌡️
Ensures a steady flow of coolant to regulate temperature. - Enhances Engine Efficiency 🚗
Helps maintain optimal performance and fuel economy. - Reduces Wear and Tear ⚙️
Prevents excessive heat damage to engine components. - Improves Longevity ✅
Regular maintenance extends the lifespan of both the pump and the engine.
Common Issues and Signs of Water Pump Failure ⚠️
A failing water pump can lead to serious problems. Watch out for these signs:
- Coolant Leaks 💦
Visible puddles under the vehicle or machinery. - Overheating Engine 🔥
Temperature gauge rising above normal levels. - Unusual Noises 🔊
Squeaking or grinding sounds from a worn-out bearing. - Steam from the Radiator ☁️
Indicates coolant isn’t circulating properly. - Loose or Wobbly Pulley 🔧
Can lead to pump inefficiency and eventual failure.
If you notice these issues, immediate inspection and possible replacement of the water pump are necessary.
Conclusion
Understanding what’s inside a water pump helps with maintenance, troubleshooting, and informed decision-making. Each component—from the impeller to the bearings—plays a crucial role in keeping your engine or industrial system running smoothly.
Regular maintenance and timely repairs ensure longevity and efficiency. If you suspect a problem with your water pump, don’t delay—check for leaks, noises, and overheating signs to prevent costly damage.
For more in-depth automotive and mechanical repair guides, explore our expert articles! 🚘💡